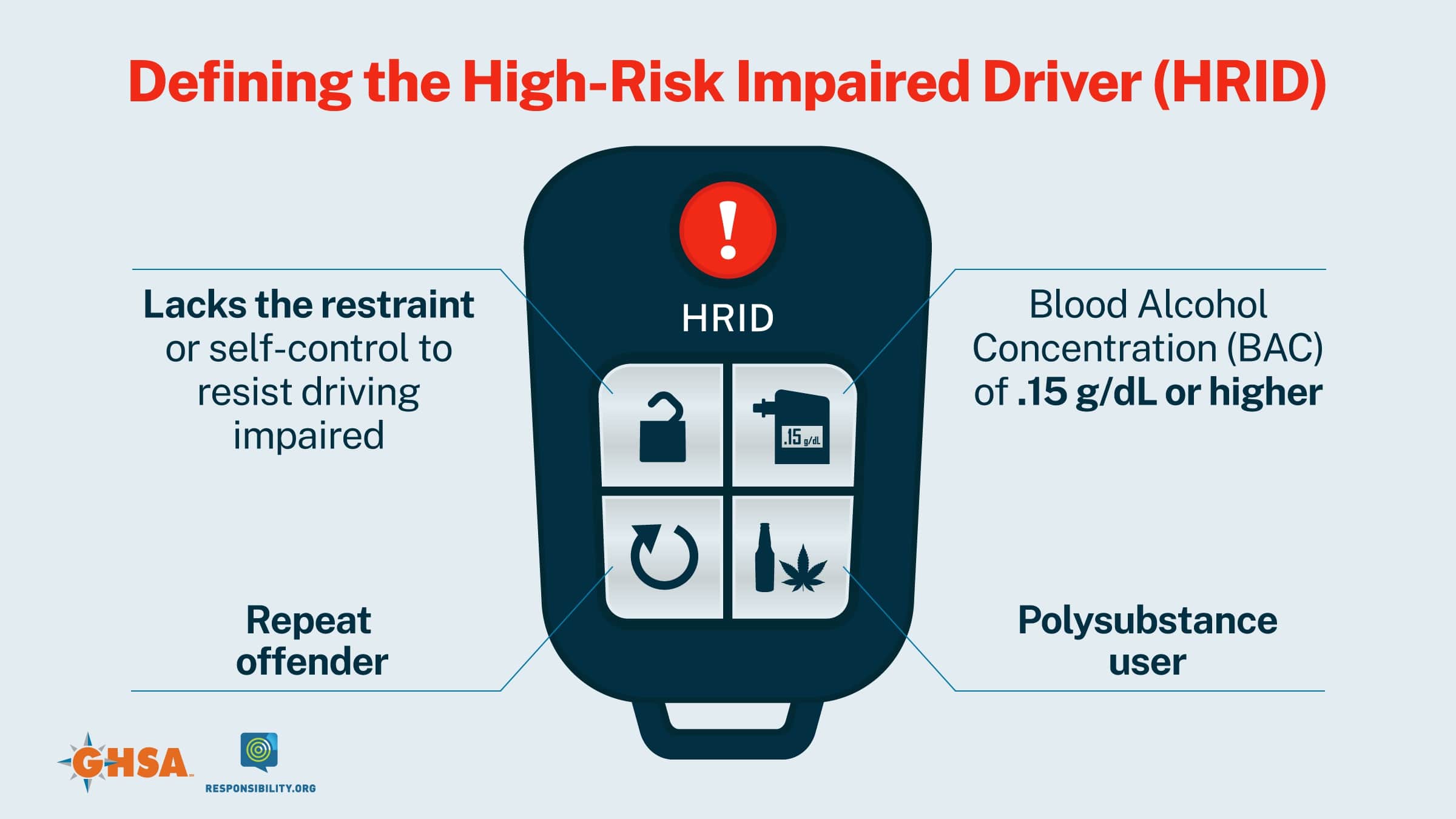
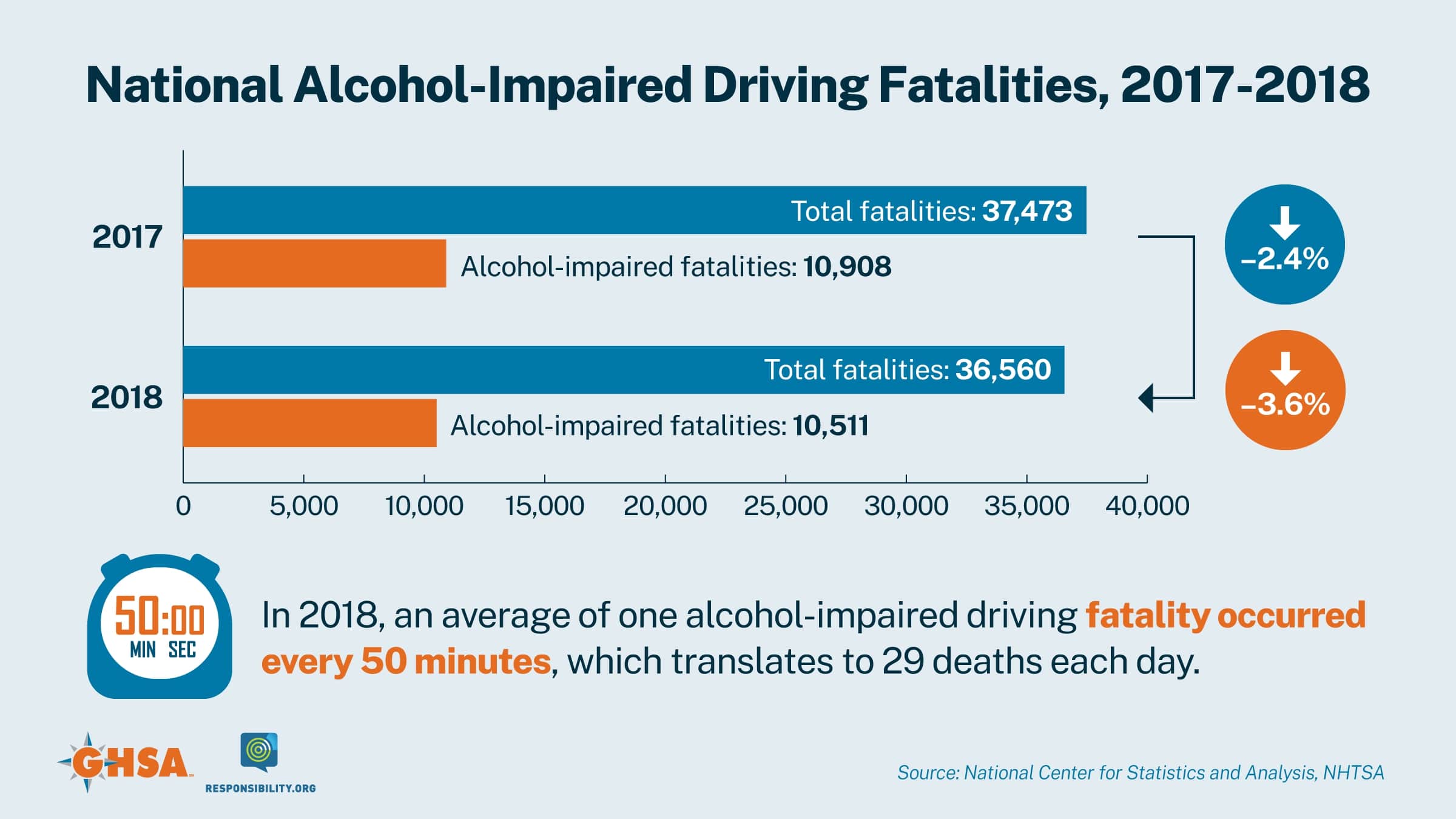
GHSA's report, High-Risk Impaired Drivers: Combating a Critical Threat, focuses on the challenges and opportunities associated with the high-risk impaired driver — a person who lacks the restraint or self-control to resist driving impaired.
A high-risk impaired driver is likely to drive with a BAC of .15g/dL or higher — or after consuming drugs or a combination of alcohol and drugs — and to do so repeatedly as evidenced by having more than one DUI arrest. Whatever the impairing substance, the high-risk impaired driver is highly resistant to changing his/her behavior despite sanctions, treatment or education and poses an elevated crash risk.
The report calls for a holistic approach to high-risk impaired drivers that focuses on the individual and the need to treat the underlying problem prompting the behavior. It makes recommendations on how SHSOs can help and provides several examples of promising approaches including DUI treatment courts, data sharing and e-warrants, toxicology labs and screening and assessments.